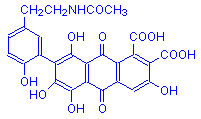
Laccaic acid A

Laccaic acid B

Laccaic acid C

Laccaic acid D
Note that laccaic acids A, B and C differ at a single point only.
Shellac Laccaic acid Xanthokermesic acid
Description
Lac is a dye, and shellac is a common wood finish. Both are obtained from the secretions of an insect found in India, Laccifer lacca (formerly Coccus lacca). The insects are embedded in the resinous secretion, forming a mass. The dye compounds are water soluble and this is used to extract them from the mass. The resinous residue is further purified to produce shellac, the wood finish.
The dyes produce red colors when used with mordants and were used for cloth, leather, and cosmetics. Lac is chemically very similar to carmine and, as the older name indicates, the insects are related to those from which carmine is obtained.
Although not used in histotechnology, lac is relevant as, over a period of time, lac has been changed to lake and is now used as a general term for metal-dye complexes.
There are four compounds found in lac, designated laccaic acids A, B, C and D. Laccaic acid A is the most abundant. Laccaic acids A, B, and C are very similar, differing at a single point, and this is illustrated in the formulas above. Laccaic acid D is also called xanthokermesic acid, and closely resembles kermesic acid in structure.
Insect Dyes
References
- Susan Budavari, Editor,
The Merck Index, Ed. 12
Merck & Co., Inc., Whitehouse Station, NJ, USA