Howell's Rubeanic Acid
for Copper Deposits
Materials
- Eosin Y, 0.1% in absolute ethanol.
- Sodium acetate, 10% aqueous.
- Stock rubeanic acid
Material Amount Rubeanic acid 50 mg Ethanol, absolute 50 mL - Working rubeanic acid
Material Amount Stock rubeanic acid 2.5 mL Sodium acetate, 10% aqueous. 50 mL
Tissue Sample
5 µ paraffin sections of neutral buffered formalin fixed tissue are suitable. Other fixatives are satisfactory.
Protocol
- Bring sections to water via xylene and ethanol.
- Place in the working rubeanic acid solution overnight at 37°C.
- Place into 70% ethanol for 15 minutes.
- Place into absolute ethanol for 6 hours.
- Lightly counterstain with alcoholic eosin.
- Rinse well with absolute ethanol.
- Clear with xylene and mount with a resinous medium.
Expected Results
- Copper – green-black granules
- Cytoplasm – pink
Notes
- Use both negative and positive controls, as occasional failures in staining occur. A suitable positive control is a liver section from a known case of Wilson’s disease. Failing that, copper may be found in liver from chronic active hepatitis.
- Copper forms a chelate with rubeanic acid, as do some other metals. Of these, cobalt and nickel may be confused with copper, so sodium acetate is added to the solution to inhibit them.
- Rubeanic acid is also known as ethanedithioamide, dithiooxamide or dithiooxalic diamide, with the formulae below. It would appear that the copper is chelated between the sulphur and nitrogen (see Kiernan).
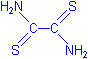
H2NCSCSNH2
Safety Note
Prior to handling any chemical, consult the Safety Data Sheet (SDS) for proper handling and safety precautions.
References
- Bancroft, J.D. and Stevens A. (1982)
Theory and practice of histological techniques Ed. 2
Churchill Livingstone, Edinburgh & London, UK. - Susan Budavari, Editor, (1996)
The Merck Index, Ed. 12
Merck & Co., Inc., Whitehouse Station, NJ, USA - Kiernan. J.A., (1999)
Histological and histochemical methods: Theory and practice, Ed. 3
Butterworth Heinemann, Oxford, UK.